Check out my first novel, midnight's simulacra!
SIMD: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Terminology (taken from SSE specs)== | |||
These do not necessarily map to the C data types of the same name, for any given compiler! | |||
* '''half precision''': 16-bit IEEE 754 floating-point (bias-15) (IEEE 754 2008 '''binary16''') | |||
* '''single''': 32-bit IEEE 754 floating-point (bias-127) (IEEE 754 2008 '''binary32''') | |||
* '''double''': 64-bit IEEE 754 floating-point (bias-1023) (IEEE 754 2008 '''binary64''') | |||
* '''long double''': 80-bit "double extended" IEEE 754-1985 floating-point (bias-16383) | |||
** not an actual SIMD type, but an artifact of x87 | |||
* '''word''': 32-bit two's complement integer | |||
* '''doubleword''', '''dword''': 64-bit two's complement integer | |||
==x86 XMM== | ==x86 XMM== | ||
===SSE5 (AMD)=== | ===SSE5 (AMD)=== | ||
Revision as of 22:48, 19 September 2009
Terminology (taken from SSE specs)
These do not necessarily map to the C data types of the same name, for any given compiler!
- half precision: 16-bit IEEE 754 floating-point (bias-15) (IEEE 754 2008 binary16)
- single: 32-bit IEEE 754 floating-point (bias-127) (IEEE 754 2008 binary32)
- double: 64-bit IEEE 754 floating-point (bias-1023) (IEEE 754 2008 binary64)
- long double: 80-bit "double extended" IEEE 754-1985 floating-point (bias-16383)
- not an actual SIMD type, but an artifact of x87
- word: 32-bit two's complement integer
- doubleword, dword: 64-bit two's complement integer
x86 XMM
SSE5 (AMD)
- Unimplemented extensions competing with SSE4, encoded using a method incompatible with VEX
- Withdrawn, converted into VEX-compatible encodings, and split into:
- FMA4: Fused floating-point multiply-add (compare Intel's FMA)
- XOP: Fused integer multiply-add, byte permutations, shifts, rotates, integer vector horizontal operations (compare Intel's SSE4)
- CVT16: Half-precision conversion
SSE4 (Intel)
SSE4a
SSE4.1
- Introduced on Penryn
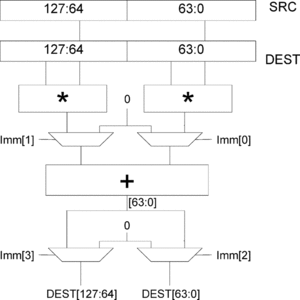
- dpps -- dot product of two vectors having four single components each
- dppd -- dot product of two vectors having two double components each
- insertps
SSE4.2
- Introduced on Nehalem
SSE3 (PNI)
- Originally known as Prescott New Instructions, and introduced on P4-Prescott
- movddup -- move a double from a 8-byte-aligned memory location or lower half of XMM register to upper half, then duplicate upper half to lower half
SSSE3 (TNI/MNI)
- Introduced with the Core microarchitecture. Sometimes referred to as Tejas New Instructions or Merom New Instructions
- pmaddwd -- multiply packed words, then horizontally sum pairs, accumulating into doublewords
SSE2
- movapd -- move two packed doubles from a 16-byte-aligned memory location to XMM registers, or vice versa, or between two XMM registers.
- movupd -- movapd safe for unaligned memory references, with far inferior performance.
- mulpd -- multiply two packed doubles. the multiplier is a 16-byte-aligned memory location or XMM register. the target XMM register serves as the multiplicand.
- addpd -- add two packed doubles. the addend is a 16-byte-aligned memory location or XMM register. the target XMM register serves as the augend.
SSE
- movaps -- move four packed singles from a 16-byte-aligned memory location to XMM registers, or vice versa, or between two XMM registers.
- movups -- movaps safe for unaligned memory references, with far inferior performance.
- mulps -- multiply four packed singles. the multiplier is a 16-byte-aligned memory location or XMM register. the target XMM register serves as the multiplicand.
- addps -- add four packed singles. the addend is a 16-byte-aligned memory location or XMM register. the target XMM register serves as the augend.
Future Directions
- AVX (Advanced Vector eXtensions) -- to be introduced on Intel's Sandy Bridge (2010) and AMD's Bulldozer (2011), and implemented within the VEX coding scheme
- The FMA instruction set extension to x86 should hit around 2011, providing floating-point fused multiply-add
- AMD appears to call this FMA4, part of what was SSE5
x87 MMX
MMX (Intel)
3DNow! (AMD)
Other Architectures
- PowerPC implements AltiVec
- SPARC implements VIS, the Visual Instruction Set
- PA-RISC implements MAX, the Multimedia Acceleration eXtensions
- ARM implements NEON
- Alpha implemented MVI, the Motion Video Instructions
- SWAR: SIMD Within a Register (bit-parallel methods)
See Also
- "Why no FMA in AVX in Sandy Bridge?", Intel Developers Forum
- SSE5 guide at AMD
- 2007-04-19 post to http://virtualdub.org, "SSE4 finally adds dot products"