Check out my first novel, midnight's simulacra!
Ergot
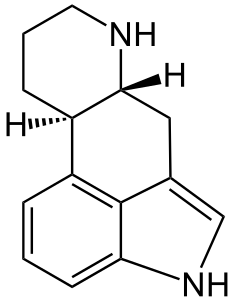
Ergot is pronounced ur-git, not er-go. Highly toxic, it ought not be consumed. Properly modified, it has many uses, primarily due to fortuitous similarity between the ergoline skeleton and the monoamide neurotransmitters (e.g. serotonin, dopamine, adrenaline)...
Ergot alkaloids ergonovine and ergotamine (and their salts) are both original List I controlled precursors under the 1970 Controlled Substances Act. Ergocristine was added to List I in 2010 (see the DEA's 2010-03 Microgram Journal). Derivatives lysergic acid and its amide ("ergine") are Schedule III controlled substances under the CSA, and ergine is a Class A precursor in the United Kingdom. Subsequent derivative lysergic acid diethylamide is an original Schedule I controlled substance, and its functional analogues (any chemical "substantially similar", as if that had any kind of precise meaning) are treated as Schedule I due to the 1986 Federal Analogue Act. Ergotamine, lysergic acid, and ergometrine (ergonovine) are all on Table I of the INCB Red List, and EU Category 1 precursors. So there's clearly something worth knowing about ergot!
Some basic terminology
- Ergot: fungi of the genus Claviceps. All Claviceps species are ergot. The most well-known member is Claviceps purpurea (Latin purpuro, purple, "to adorn/beautify"), the rye ergot fungus, which is parasitic on grasses and cereals (especially rye, Secale cereale).
- A Claviceps spore infects a flowering grass or cereal's floret. Upon connection to the vascular bundle, soft white sphacelia tissue develops. This hardens and dries into a sclerotium in the destroyed floret's husk.
- Alkaloids and lipids accumulate in the sclerotium. Dry, mature claviceps purpurea sclerotium consist of about 2% ergot alkaloids by weight. Claviceps africana also contains substantial alkaloids.
- Petri-grown Claviceps sees best results with potato dextrose or malt extract agar.
- Alkaloid: Basic (high-pH) naturally-occurring organic compounds containing nitrogen. The "true alkaloids" are biosynthesized from amino acids and contain nitrogen in a heterocycle (a cyclic structure containing more than one element).
- Indole: The aromatic heterocycle C8H7N. Bicyclic pair of benzene (C6H6) and pyrrole (C4H4NH) sharing an edge. A biosynthetic precursor to the indole alkaloids, including the amino acid tryptophan and 3-indolepropionic acid (IPA).
- Tryptophan: An essential amino acid (one which cannot be biosynthesized in humans), and a precursor in humans of serotonin, melatonin, and vitamin B3. Clostridium sporogenes in the human gut metabolizes tryptophan into indole.
- Ergoline: the tetracyclic structural skeleton (C14H16N2) shared by ergoline alkaloids. Also a tanning bed by JK Products (pronounced differently).
Ergoline path (biosynthesis of the ergot alkaloids)
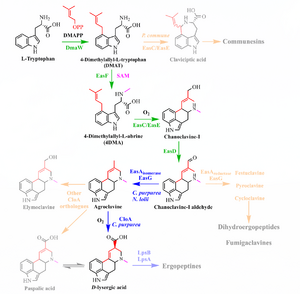
The road to the ergolines begins with L-tryptophan and culminates in D-lysergic acid. The ergoline skeleton is complete in agroclavine (and indeed apparent in its three sibling daughters of chanoclavine). Note that if one is interested in the water-soluble lysergamides, ergopeptines are not a necessary precursor. Ergolines are generally classified as one of:
- Clavines (not generally psychoactive)
- Ergopeptines (ergopeptides). Water-insoluble.
- Ergotoxines: ergocristine, ergocornine, ɑ- and β-ergocryptine
- Ergotamine group: ergotamine, ergovaline, ɑ- and β-ergosine
- Lysergamides (lysergic acid amides). Water-soluble. Of particular interest are:
- Ergine (LSA, D-lysergic acid amide)
- LSD-25 (LSD, D-lysergic acid diethylamide)
Note that ergine occurs naturally in some vines of the Convolvulaceae family (Hawaiian baby rosebud aka Argyreia nervosa, morning glory aka Ipomoea tricolor, and ololiúqui aka Ipomoea corymbosa), and is thus an ergoline alkaloid. There is no known natural source of the synthetic LSD-25. LSA is a mild psychedelic. LSD is one of the most potent psychedelics known to man.
WRITEME provide details of gene coding for enzymes
- L-tryptophan C11H12N2O2 -> (prenylation via DMAPP from mevalonic acid, catalyzed by DMATS)
- DMAT(S): dimethylallyltryptophan (synthetase)
- 4-L-DMAT -> (N-methylation via SAM, catalyzed by EasF)
- 4-DMA-L-abrine -> (decarboxylation+oxidation via EasC, catalyzed by EasE)
- Chanoclavine-I -> (oxidation via EasD)
- Chanoclavine-I-aldehyde (a D2 dopamine receptor stimulant) ->
- Agroclavine ->
- Alternate branch: Elymoclavine (C16H18N2O) ->
- Paspalic acid -> (see below)
- D-Lysergic acid (DLA).
Chanoclavine-I-aldehyde branches to festuclavine, pyroclavine, and cycloclavine (in addition to agroclavine), leading to the dihydroergopeptides and fumigaclavines. In addition to DLA, agroclavine branches to emiloclavine (also seen as emyloclavine) and thus paspalic acid.
Paspalic acid
Paspalic acid is an isomer of lysergic acid, and will spontaneously convert. Jean-Claude Gaullier's 2000 patent specifies a high-yield (81.6% RRi, 2.8% iso-LA) isomerization using a tetra(C1-C6)alkylammonium hydroxide. In that same patent, he describes previous isomerizations using 2N sodium hydroxide or 0.5N potassium hydroxide, reporting 59.3% RRi with NaOH (6.8% iso-LA) and 49.8% RRi with KOH (1% iso-LA). These isomerizations were described in the Swiss journal Helvetica Chimica Acta in 1981 and 1964, respectively. Cvac + Mojczek claimed to do even better purity-wise in 2005 by following the metallic hydroxide with a methanol wash.
Extraction of ergopeptines from ergot
Stoll patented the isolation of ergotamine tartrate in 1918 at Sandoz. WRITEME
Bioengineered ergoline
WRITEME
D-lysergic acid
Lysergic: discovered via hydrolysis of ergotamine. A Table I precursor under the UN Convention Against Psychotropic Substances and a Schedule III controlled substance. About 15 tons of DLA (also seen as (+)-lysergic acid) are legitimately manufactured each year, primarily from submerged fermentation of special strains of Calviceps purpurea but also from field harvests.
The ergopeptides are biosynthetic derivatives of DLA, but DLA is a synthetic derivative of the ergopeptides. DLA was first isolated by hydrolysis of ergot alkaloids in the 1930s (Jacobs & Craig, "The Ergot Alkaloids: II. The Degradation of Ergotinine with Alkali. Lysergic Acid", Journal of Biological Chemistry 1934). It was first synthesized by Woodward's team in 1956 starting from 3ß-carboxyethylindole (Kornfield et al, "The Total Synthesis of Lysergic Acid", Journal of the American Chemical Society 1956-07), and numerous processes have been published since: see this 2022 review for full details. The manufacture of LSD requires DLA, which has been historically hydrolyzed from bulk ergot alkaloids due to the difficulty of other syntheses. Controlled biosynthesis ought cease at DLA; should you have the opportunity to acquire DLA, you're ready to go to town and/or prison.
Stereoisomers
WRITEME
Production from agroclavine
WRITEME
Production from ergopeptides
WRITEME
Production from lysergamides
WRITEME
D-lysergic acid diethylamide
Hoffman first synthesized LSD ("Lysergsäurediethylamid") 1938-11-16 at Sandoz Pharmaceuticals. On 1943-04-19, he accidentally ingested about 250 micrograms, and discovered its potent effects. It was the twenty-fifth substance synthesized in a program of systematically exploring the ergot alkaloids, hence the name LSD-25.
Production from DLA
WRITEME
Pharmacokinetics
WRITEME
Testing
WRITEME
Mass spectrometry
Practical matters
WRITEME
Experimental
Some things I'm not yet sure about.
Back-synthesis from DLA derivatives
Remember those 15 tons of legitimately-produced lysergic acid? That's in addition to about ten tons of ergotamine alkaloids; i.e. your Cafergot (ergotamine tartrate + caffeine) and Syntometrine (ergometrine + oxytocin) aren't counting against that total. So there's about 25 tons of pharmaceutical precursor being generated each year. Where is it all going? Is it going anywhere where we can get it back?
- Sermion (nicergoline)
- Parlodel (bromocriptine, ergocryptine derivative)
- ...
Can we do anything with ergosterol (available from lanosterol)?
External links
I'm not going to link to all the various papers and patents for synthesizing DLA, as they're well-covered by review articles.
- Methods of Lysergic Acid Synthesis. Jastrzębski et al. Molecules 2022-10.
- Reconstituting the complete biosynthesis of D-lysergic acid in yeast. Wong et al. Nature Communications 2022-02.
- Biosynthesis, total synthesis, and biological profiles of ergot alkaloids. Tasker & Wipf. The Alkaloids: Chemistry and Biology 2020.
- The Chemistry of Peptide Ergot Alkaloids. Komarova & Tolkachev. Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal 2001-02, translated 2001-09.
- Ergotamine Production in Submerged Culture and Physiology of Claviceps purpurea. Amici et al. Applied Microbiology 1967-05.
- List of Precursors and chemicals frequently used in the illicit manufacture of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances under International Control. International Narcotics Control Board 2022-01. Also known as the "Red List".
- Tryptamine and Ergoline Chemistry on the Hive (archived at Erowid)