Check out my first novel, midnight's simulacra!
ESP8266: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Tags: mobile web edit mobile edit |
Tags: mobile web edit mobile edit |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ESP8266 ESP8266] on Wikipedia | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ESP8266 ESP8266] on Wikipedia | ||
* [https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp8266-technical_reference_en.pdf ESP8266 Technical Reference | * [https://www.espressif.com/sites/default/files/documentation/esp8266-technical_reference_en.pdf ESP8266 Technical Reference] | ||
[[CATEGORY: Hardware]] | [[CATEGORY: Hardware]] | ||
Revision as of 05:39, 26 November 2022
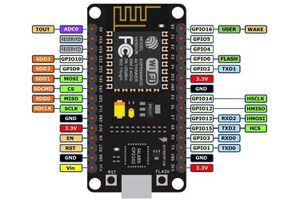
A series of 32-bit microcontroller units from Espressif, followed by the ESP32. The first generation of the NodeMCU SoC was based around ESP8266.
Notes
- There is only one (10-bit) ADC, and it reports values between [0, 1], not [0, 3.3]. This is not a scaling--the input voltage should not exceed 1V.
- This is not true for e.g. the NodeMCU, which applies a divider network to scale the 3.3V down to 1V. This allows supplying 3.3V to the external device.
- On the NodeMCU, this ADC can read the battery voltage instead of a connected external device. This is set in firmware.
External links
- ESP8266 on Wikipedia
- ESP8266 Technical Reference