Check out my first novel, midnight's simulacra!
XDP
In the beginning, there were applications slinging streams through the packetizing Honeywell DDP-516 IMPs, and it was good. Then multiple applications needed the network, and needed it in different ways. Then the networks needed walls of fire, and traffic which was shaped. Some called for the Labeling of Multiple Protocols, and others called for timestamps, and still others wanted to SNAT and DNAT and also to masquerade. And yea, IP was fwadm'd, and then chained, and then tabled, and soon arps and bridges too were tabled. And behold now tables of "nf" and "x". And Van Jacobson looked once more upon the land, and frowned, and shed a single tear which became a Channel. And then every ten years or so, we celebrate this by rediscovering Van Jacobson channels under a new name, these days complete with logo.
Most recently, they were rediscovered under the name DPDK, but the masters of the Linux kernel eschewed it, and instead rediscovered them under the name XDP, the eXpress Data Path, expressed using eBPF programs. XDP was added to Linux 4.8 and has been heavily developed since then, and is often seen together with iouring, especially with the new AF_XDP family of sockets.
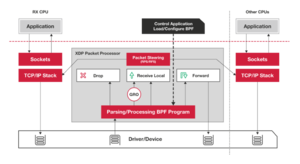
XDP is used to bypass large chunks of the Linux networking stack (including all allocations, particularly alloc_skb()), especially when dropping packets or shuffling them between NICs.
Using XDP
An XDP program is an eBPF program invoked for each received packet which runs either:
- early in the kernel receive path, with no driver support (Generic Mode)
- from the driver context, without any kernel networking stack touches (requires driver support) (Native mode)
- on the NIC itself, without touching the CPU (requires hardware+driver support) (Offloaded mode)
Offloaded mode can theoretically beat native mode, which will usually beat generic mode. XDP programs are specific to a NIC, and most easily attached using xdp-loader. Lower-level functionality is available from libxdp, and below that is pure eBPF machinery. Multiple XDP programs can be stacked on a single interface as of Linux 5.6 (multiprog requires BTF type information, created by using LLVM 10+ and enabling debug information).
xdp-loader status will list NICs and show any attached XDP programs.
Note that XDP runs prior to the packet socket copies which drive tcpdump, and thus packets dropped or redirected in XDP will not show up there. It's better to use xdpdump when interacting with XDP programs; this also shows the XDP decision made for each packet.